Industrial Networking Advice
PLC network to HMI/SCADA, then to cloud/smartphones?
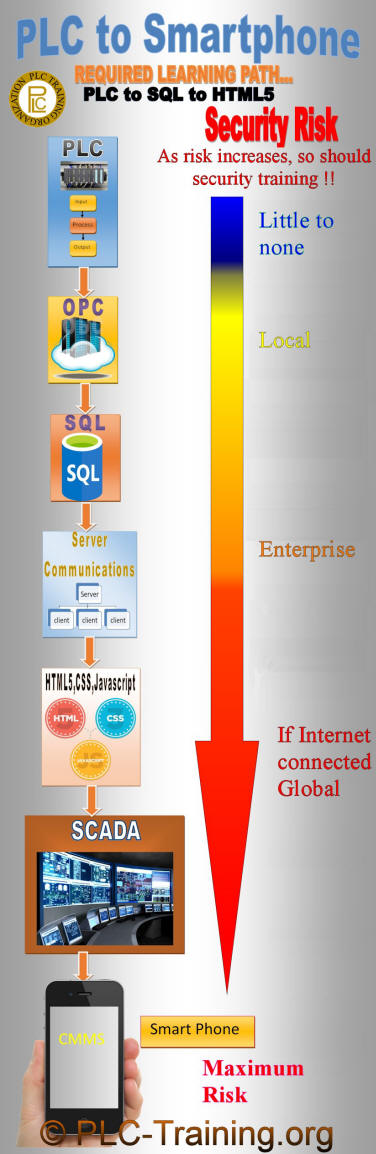
To the right is an infographic with the recommended learning path to get data from PLCs to Smartphones and other devices in between. The fields of study required are...
- PLC Networking
- OPC UA
- SQL
- Client/Server Communications
- HTML5, CSS, JavaScript
- HMI SCADA
- Smartphone Programming
You will notice in the infographic that Security training is emphasized, yet not in the list of fields to study. That is because each field of study will have its specific network security curriculum to be mastered. You will also note that with each technology the data travels through, the security concerns increase and therefore require greater study and competence. Also, note that before taking on training and a project of this nature, one should have at least 1 year of experience in the industry and a 2-year associate's degree in this field as a minimum.
Below are a few more details on each field of study, including a summary of the technology and helpful tips in the learning path for PLC network communication to PC HMI/SCADA to the Smartphone or cloud. More accurately, PLC to SQL to Smartphone. Start with PLC network and communication protocols and methods, then expand to HMI-SCADA, to SQL (and brand-specific topics like RSLinx OPC server), Excel OPC client, HTML5, and you’re ready for Smartphone applications.
PLC Networking Training:
Of course, before learning a particular PLC network, one must first master the PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) as indicated by the PLC-Training.org 10 PLC learning phases. Also, as shown on this site, the PLC should be mastered before going on to master the PAC (an Industrial Computer that emulates a PLC). Unlike networking computers, where only data and software are at risk in the event of mistakes or security breaches, PLCs or PACs pose a greater threat, as they can also damage both humans and machines. When networking a PLC or a PAC, the difference between the two and the importance of distinguishing between the two becomes even clearer. You can learn more about the various CIP and RS-485 PLC communication types in that section.
A PLC is a microprocessor device used to control equipment via an electrician-friendly Ladder Logic programming language. Often, those not properly trained will also refer to an Industrial Computer (dual full processors) as a PLC, instead of its proper term, PAC (Process Automation Controller). ARC Advisory Group first defined the term PAC in 2001. However, the PAC includes PLC-like capabilities. The PAC hardware architecture and software are more user-friendly to IT and Computer Programmers. Differences include multitasking, multiple processor modules per rack, etc. PACs also have more advanced programming languages, such as structured text. The differences go on, distributed control system (DCS), Tag-based addressing, motion control, and standard PC networking like Ethernet.
OPC UA Training:
OPC standard is a software interface, the Open Platform Communication protocol standard that allows Windows programs to communicate with industrial hardware devices. Today's version, OPC UA (Unified Architecture), is a more secure cross-platform architecture, not limited to Windows only. OPC UA (OLE for Process Control) is the latest, most powerful communications protocol for the industry. OPC UA facilitates data transfers quickly and effectively. (OLE is Object Linking and Embedding)
External and internal threats are concerns in critical control systems. OPC Security is learned and applied to prevent accidental or intentional unauthorized OPC data access. OPC Security is a standard provided and maintained by the OPC Foundation.
The recommended minimum OPC UA training ...
- Basic Concepts of OPC
- OPC UA Client/Server Configuration & Architecture
- OPC Redundancy DA and HDA
- OPC Tunneling Technology
- OPC Alarms and Events
- Windows Security
- OPC Security
- XML Overview
- COM and DCOM Configuration Basics & Troubleshooting
- SCADA applications basics using OPC Alarms and Events
SQL Training:
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a programming language used to manage data in a relational database on a server. Getting data from a PLC into a SQL database may require even more advanced SQL training. A way to get process values from the production into your spreadsheet, ERP system, or other PC software. (Also, a way to expand your PLC memory and be a historian.) A more common approach when the device is a PLC is to use MS Visual Basic programming language or macros, OLE with MS Access or MS Excel, Excel OPC client, etc. You always need vendor-specific solutions. For instance, with Rockwell, the solution would be RSLinx OPC Server, which comes with vendor-specific complexities, such as requiring the Professional edition or better. Data is written and queried to/from the SQL database server via Ethernet.
But most automation controller vendors provide an add-on SQL function block for their PACs. Some PAC vendors/models may only communicate with the SQL relational database using an "unconnected" connection, while others use the standard "connected" connections. On the HMI SCADA side, reading from and writing to the SQL database is much easier as it is just computer-to-computer communication, formats, and protocols. So if you already know how to get data from PLC to HMI SCADA, it will be much easier. With PACs, vendors, and third-party software providers, you can create integration software packages that simplify design. For example, PLCSQL Link software eliminates the need for OPC servers or VB Scripts. While connecting a PLC or PAC to an SQL database can get complicated, the good news is that the programming language is as easy as ladder logic, with basically five instructions. SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT, and WHERE. You can get free online SQL training from W3. Also, if you want to dive deeper into SQL and prefer learning from videos, Guru99 is a great resource.
Organizations need to apply best practices to the entire software development lifecycle, user interfaces, networking, and databases. 92% of all security vulnerabilities are now considered application vulnerabilities and not network vulnerabilities (according to NIS). The common SQL injection security vulnerability must be thoroughly understood and accounted for. The SQL attack occurs when a web application submits and executes a SQL command, thereby exposing the back-end database.
Client/Server Communications:
As well as learning the basics of OPC Server communications and SQL server communications, more importantly, one must learn the basics of common server operating systems (OS), Linux, and Windows. We say more importantly, because once machine data is transmitting bi-directionally over computer networks, your security risk increases many times. When a computer network connects to the world outside your plant's physical location, the security risk increases significantly. To oversimplify PLC Industrial Network protocol - complicity(PAC plant internal Ethernet risk2)2 - PAC external network risk2x2 - PAC external network via internet/cloud/mobile risk2x2x2 ...
Security Risk...
- PLC only industrial network protocol - virtually none
- PLC/PAC internal Ethernet network - low risk
- PLC/PAC external private Ethernet network - medium risk
- PLC/PAC external Ethernet 'cloud' network - high risk
- PLC/PAC internet or mobile network - extremely high risk!
Due to the high risk of damaging humans or million-dollar equipment, working in this area of system integration requires at least a Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE) certification, or, at the very least, close collaboration with a certified network administrator. (LPIC-2 if working with Linux server OS) It's alarming to see the number of plant maintenance and engineering professionals in our industry's online discussion forums struggling with networking PLC/PACs without the recommended certifications. Relying on anonymous forum members they do not know, with unknown and unverified certifications, for advice on how to network their company's PLCs to their Smartphone! It's a hacker's virtual who's who of soft targets list. Low-hanging fruit is primarily due to industrial companies not having or enforcing company policies concerning their PLCs and industrial controls. Federally regulated industries, such as food & drug, utilities, and transportation, are exceptions to the rule, as they are subject to mandated policies and procedures.
HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript Training:
All modern web applications, including websites, are designed using HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript to enhance security and ensure compatibility across multiple devices. Using these standards, you write the program and create the user interface once; it will work correctly in all modern browsers, tablets, and Smartphones. If you were designing a website or computer application, certification may not be necessary. But if creating a live machine interface like HMI SCADA, certification is recommended. HTML5 Developer Certification proves fundamental knowledge of web development using HTML5.
In getting HTML5 certified, you should learn about most security considerations. Additional advice includes turning off your server signature, blocking directory browsing, blocking access from libwww-perl, and ensuring your DNS server uses an SPF record.
Recommended for Designing Industrial HTML5 Applications...
- Introduction to designing user interfaces
- CSS basics and managing user interfaces
- JavaScript basics, functions, variables and APIs
- JavaScript animations, canvas/SVG and user data handling
- XML, SQL, PHP, W3.CSS
HMI SCADA Training:
HMI and SCADA training requirements have already been covered on this site, as HMI SCADA Training is the 10th learning phase on this site. However, since this is our first encounter with PLC-Training.org through this white paper, we'll briefly explore the topic. Please note that you should also explore the section linked above, along with its associated HMI SCADA Training Best Practices section, for those who have not stopped to think about it, first, the basics. Acronyms in our industry are necessary to differentiate between devices. For instance, PAC stands for an industrial computer architecture, which is distinct from a single dedicated microprocessor like the PLC. But other times in our industry, acronyms and terminology can hide important basic facts. Like the "internet" and the "cloud". Often, people lose sight of the fact that when their sensitive data is on the 'secure cloud', it transfers from the 'cloud' via the Internet. (A website stores the data on the server, accessed via the worldwide network called the Internet. The 'cloud' does the same. The basic difference is that one is open to the public, the other is not.)
45% of data breaches in 2023 were cloud-based, according to an IBM report.
HMI (Human Machine Interface) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) acronyms also made an important distinction. SCADA was an HMI with Data Acquisition. Another essential fact about SCADA is that it ushered in the concept of machine data on local computer networks. However, the two acronyms, along with the phrase "SCADA systems", also pushed to the back of decision-makers' minds that HMI SCADA is essentially just computer software running on a computer network. Which, once you think of it that way, the first thought and concern should be, computer/software equals virus susceptible. Losing sight of this fact is what made the Stuxnet virus able to damage a nuclear plant. Nowadays, as computer technology becomes less expensive, HMIs integrated into machines are becoming SCADA software by definition, yet referred to as HMI, making the risk even less thought about. Many in the non-federally regulated industries have less enforced security procedures than you might have on your computer at home. Many facilities lack backups of all their HMI programs, often due to understaffing, but also because they do not consider HMIs to be computers. It is usually similar to the process of backing up a PLC program.
Smartphone Programming Training:
There are two approaches to getting your HMI SCADA onto the Smartphone: as a web page or as an App. The approach you take will determine the Smartphone programming training you need. Regardless of the approach, you will first need to be certified in mobile app certification and cloud networking. If you decide to use the web page approach, see the HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript training requirements above.
Then, depending on which mobile platform you will be programming on, you will seek programming training for that specific platform, like the two most popular, Android and iOS (Apple). We only linked to the Android mobile app certification training above because it is the most frequently requested by employers. Another advantage of being certified in Android OS programming is that the OS works with Multiple Vendors, and the core programming language is Java, so a smaller learning curve if you did the JavaScript training recommended above in the HTML5 section. If you are seeking iOS (Apple) programming training, it uses the Objective-C programming language and is compatible only with Apple products. So, as with all things Apple, you will be limited in your applications, capabilities, options, and job opportunities.
Besides the HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript training requirements mentioned above, you will need a bachelor's degree in software engineering. To include object-oriented programming (OOP), Java programming, Objective-C and C++ programming, user-interface (UI) design, database & OS fundamentals, to name a few.
Additionally, the need for extensive education on mobile security vulnerabilities requires thorough study and consideration. In short, mobile security vulnerabilities are design or implementation errors that expose mobile device data to interception and retrieval by attackers. Mobile code security vulnerabilities can also expose the mobile device or the cloud applications used from the device to unauthorized access. An industrial equipment designer must thoroughly understand the Security vulnerabilities of the infrastructure layer, the hardware, the operating system, and the application layers.
~ PLC Networking Summary ~
Essential Fields of Study for PLC Networking
To effectively engage in PLC networking, it is crucial to understand a variety of fields, including OPC UA, SQL, and various programming languages such as HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript. These subjects form the backbone of modern industrial automation and communication systems, equipping professionals with the necessary skills to integrate PLCs with HMI and SCADA systems.
For instance, knowledge of SQL is vital for managing databases that interact with PLCs. At the same time, proficiency in HTML5 and JavaScript is essential for developing user interfaces that can run on smartphones and other devices. A comprehensive understanding of these areas not only enhances technical capabilities but also ensures that professionals can manage the complexities of modern industrial environments.
The Importance of Security Training in PLC Systems
Security training is a critical component for anyone working with PLC systems, as these systems often control crucial industrial processes. Understanding potential vulnerabilities and implementing security measures can prevent catastrophic failures and protect both personnel and equipment from harm.
For example, professionals should be familiar with best practices such as disabling directory browsing, using SPF records for DNS servers, and regularly backing up HMI programs. These measures help mitigate risks associated with cyber threats, ensuring that the integrity of industrial operations is maintained.
Client/Server Communications in Industrial Automation
In the realm of industrial automation, mastering client/server communications is essential. Master the basics of OPC Server communications and SQL Server interactions. Familiarize oneself with operating systems commonly used in industrial settings, such as Linux and Windows.
Effective communication between machines and servers is vital for real-time data exchange and operational efficiency. For instance, knowledge of how to configure server settings and manage network security can significantly reduce the risks associated with data breaches and system failures, making it imperative for professionals to stay updated on these topics.
Designing User Interfaces for Industrial Applications
Creating user interfaces for industrial applications involves a unique set of challenges and considerations. Professionals must ensure that interfaces are not only functional but also user-friendly. The designer takes into account the diverse environments when designing the application.
Utilizing standards like HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript allows developers to create responsive designs that work across various devices. Additionally, understanding user interface design principles, such as accessibility and usability testing, is crucial in developing applications that meet the needs of operators and engineers in the field.
